Farm Size and Power Costs
Average power and equipment costs by farm size is displayed in Table 1 for 5 periods in time. Power and equipment costs averaged higher for the smallest and the largest farm sizes. Average power and equipment costs do not show a trend for size categories in the middle ranges. In 2019, the lowest average power and equipment cost was $134 per acre for farms between 2,001 and 3,000 acres. The highest cost was $168 for farms with 500 or fewer acres.
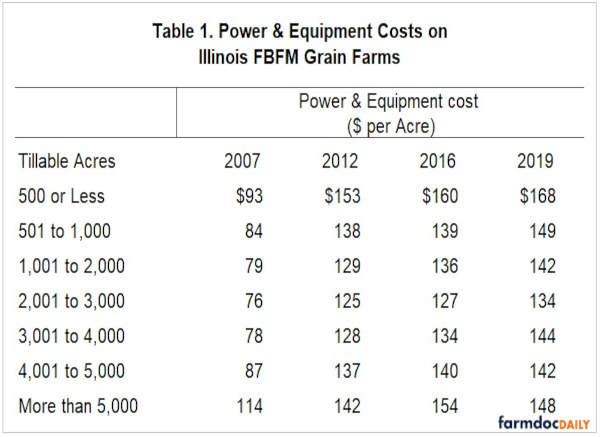
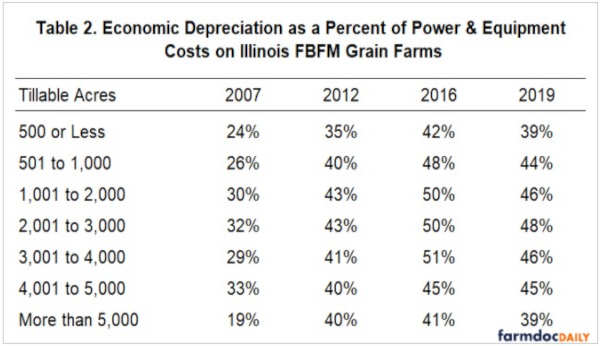
Table 2 shows economic machinery depreciation as a percent of total power and equipment costs by farm size. As you can see, there is not much difference in the percent of economic machinery depreciation by farm size. However, the percent has increased on average about 10% every five years since 2007 until 2019 where it has begun to decrease. The average economic depreciation as a percent of total power and equipment costs was 29% in 2007, 41% in 2012, 48% in 2016, and 44% in 2019. It is interesting to note that size groups with the largest power and equipment costs had the lowest percent of that cost from economic depreciation and vice versa.
Power Costs and Profitability
Lower power and equipment costs tend to lead to higher profitability. For this study, profitability is measured by per acre management returns. Management returns equal revenue minus economic expenses, with economic expenses including costs for unpaid labor and equity capital invested in the operation. Table 3 shows management returns by ranges of power and equipment cost for different points in time.
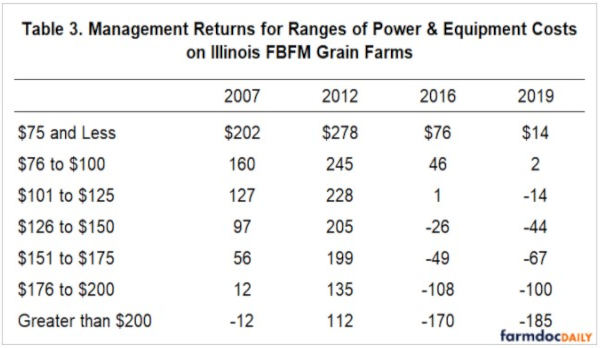
In 2019, farms that had power and equipment costs of $75 and less per tillable acre averaged management returns of $14 per acre. As power and equipment costs increased, average management returns decreased. For power and equipment cost categories between $76 and $100 per acre, management returns were $2 per acre. For farms with power and equipment costs above $200 per acre, management returns averaged a negative $185 per acre.
In general, a strong link exists between power and equipment costs and management returns. Farms that have lower power and equipment costs tend to have higher profits. Controlling costs, including power and equipment costs, is a key in increasing farm profitability.
Summary
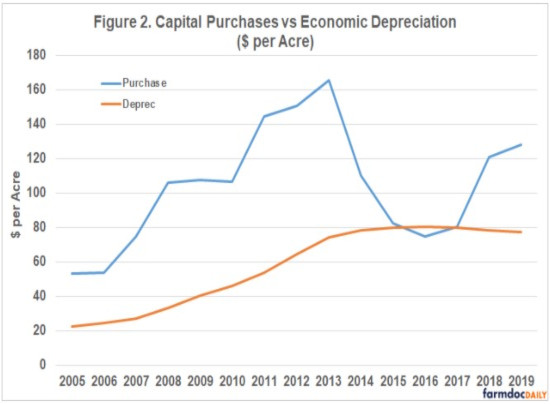
Power and equipment costs on Illinois FBFM grain farms increased quickly during the run-up in grain prices in the mid-2000’s. The main driver was economic machinery depreciation because of increased capital purchases. Most machinery is depreciated over 10 years for economic depreciation. We have begun to see economic depreciation begin to level off as capital purchased decreased from 2013 to 2017. There is a strong connection between power and equipment costs and profitability because as power and equipment costs decrease, profitability tends to increase. Therefore, power and equipment costs are worth looking into when trying to cut costs. However, in 2019, 44% of this cost was due to economic machinery depreciation, which will be slow to change thus large cuts will need to be made to the other components of power and equipment costs to make a more current impact on costs.
The author would like to acknowledge that data used in this study comes from the local Farm Business Farm Management (FBFM) Associations across the State of Illinois. Without their cooperation, information as comprehensive and accurate as this would not be available for educational purposes. FBFM, which consists of 5,500 plus farmers and 65 professional field staff, is a not-for-profit organization available to all farm operators in Illinois. FBFM field staff provide on-farm counsel with computerized recordkeeping, farm financial management, business entity planning and income tax management. For more information, please contact the State FBFM Office located at the University of Illinois Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics at 217-333-8346 or visit the FBFM website at www.fbfm.org.
Source : illinois.edu