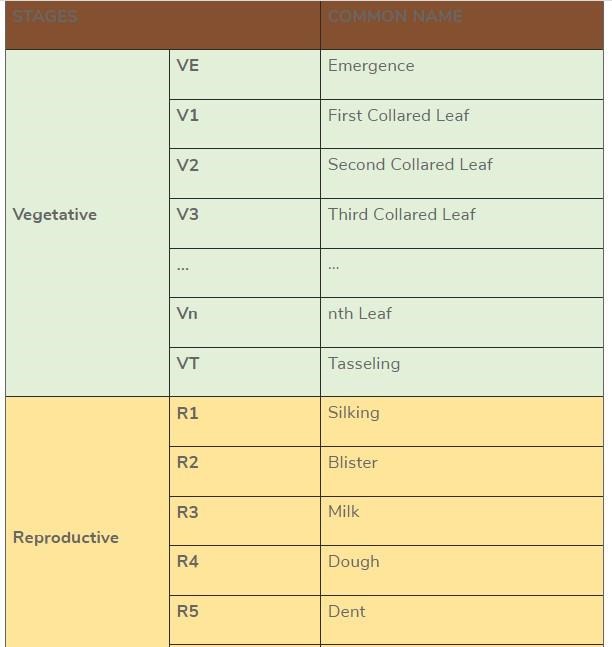
When it comes to crop management, one should focus on development as a more precise crop reference instead of growth. At later vegetative stages (after V10), younger leaves have often senesced, and the split-stalk approach may need to be taken to accurately stage plants (i.e., plants do not stay at the V12 stage until tasseling). This video shows staging using the split-stalk technique.
From planting to physiological maturity, plant structures initiate and grow at different stages (Figure 1). In the case of modern hybrids, it is common to see silks emerge (R1) before tassels fully emerged (VT) as this can improve pollination. Adverse conditions such as drought, heat, off label applications during any of these processes can negatively impact the crop and ultimately affect yields.
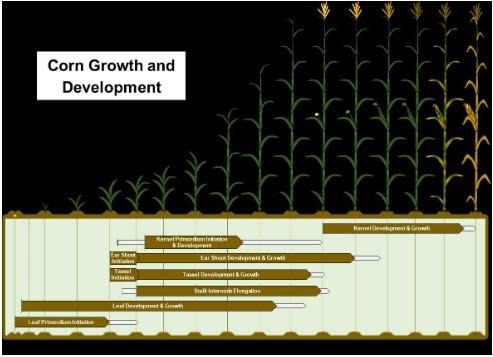
Figure 1. Corn growth and development from planting and germination (G) to physiological maturity (R6). Brown arrows indicate the primary period, and gray arrows indicate possible variations for each event. Source: Ortez et al., 2022 (Crop, Forage & Turfgrass Management, accepted, in production).
An adequate understanding of stages in corn is essential when planning different activities in the growing season—for example, fertilizer, herbicide, insecticide, and fungicide applications. Additionally, a good follow-through of corn staging can help understand when critical events occur, for example, drought stress linked to a reduction in kernel fill (i.e., kernel weight) towards the end of the season.
Source : osu.edu