How Worried are US Consumers about Climate Change?
We asked participants how worried they were about climate change. Over 75% of those surveyed said they were either very worried (33.9%) or somewhat worried (42.6%), whereas 15.9% said they were not very worried and only 7.7% said they were not worried at all.
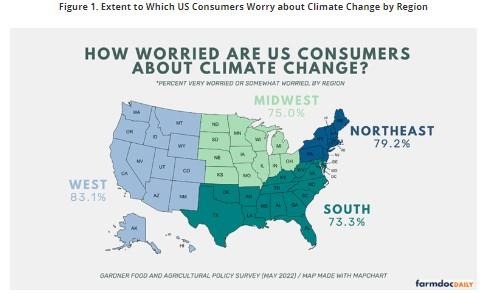
Across regions, US consumers’ levels of worry differ. We find that participants in the West indicated they were very worried (38.1%) and somewhat worried (45.0%) at the highest rate, followed by participants in the Northeast (36.7% and 42.5%, respectively), Midwest (32.9% and 42.1%, respectively), and the South (31.3% and 42.0%, respectively). Participants in the Midwest had the highest rates of being not at all worried (9.6%) followed by participants in the South (8.6%). Figure 1 shows the percent of participants that are very worried or somewhat worried by region. Differences across regions may be due to the current exposure to climate changes’ impacts, for example drought and forest fires in the West and more intense rainfall in the Northeast (e.g., USGCRP, 2018; Walthall, et al., 2012). Regional differences could also be explained in part by political differences across regions, as feelings about climate change differ across political parties (e.g., Hornsey, et al. 2016).
Figure 1. Extent to Which US Consumers Worry about Climate Change by Region
Climate Change & the Food System
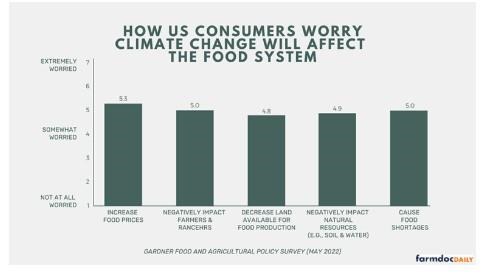
We also asked participants to rate the extent to which they were worried about climate change affecting several aspects of the food system, on a scale from 1 (not at all worried) to 7 (extremely worried). In particular, we asked about climate change increasing food prices, negatively impacting farmers and ranchers, decreasing land available for food production, negatively impacting natural resources like soil and water, and causing food shortages. Figure 2 illustrates the results. On average, US consumers were more than somewhat worried about all these potential impacts of climate change on the food system (ranging from 4.8 to 5.3). Consumers were most worried about climate change increasing food prices (5.3), negatively impacting farmers and ranchers (5.0), and causing food shortages (5.0).
Figure 2. US Consumers’ Average Level of Worry about How Climate Change Will Impact the Food System (1=Not at All Worried and 7=Extremely Worried)
Across regions, the results are quite similar and are summarized in Table 1. The mean worry values for climate change decreasing available land for food production varied the most with the Midwest being least worried (4.6) and the Northeast being most worried (5.0).
| Table 1. US Consumers’ Average Level of Worry about How Climate Change Will Impact the Food System (1=Not at All Worried and 7=Extremely Worried) |
| | Northeast | South | Midwest | West |
| Increase food prices | 5.5 | 5.2 | 5.3 | 5.4 |
| Negatively impact farmers and ranchers | 5.1 | 4.9 | 4.9 | 5.1 |
| Decrease land available for food production | 5.0 | 4.7 | 4.6 | 4.8 |
| Negatively impact natural resources | 5.1 | 4.8 | 4.8 | 5.1 |
| Cause food shortages | 5.2 | 4.9 | 4.9 | 5.1 |
Concluding Thoughts
The food system continues to feel the impacts of climate change and be at the center of much of the climate change policy debates. In our quarter 1 survey results, we find that the public is quite worried about climate change’s impacts on the food system – from increasing food prices to negatively impacting farmers and ranchers. The impacts of climate change on the food system will continue to be monitored over time, as well as evaluating public support for a variety of climate change policies.
Source : illinois.edu