The ideal timing for fungicide applications to control FHB (Figure 1) is when 50% of primary tillers reach early anthesis (Feekes 10.5.1). In other words, when anthers begin appearing from the middle third of the spikelet.
Obviously, ideal timings can be very difficult to carry out. Previously, several academic field crop pathologists compiled 19 years of results from applications of Prosaro and Caramba fungicides to wheat at three different timings. Applications were at heading (or pre-anthesis), anthesis, or 5 to 7 days after anthesis (Paul et al. 2018). Table 1 is adapted from their manuscript and shows results pertinent to winter wheat production. As expected, applications at anthesis were most effective and provided 52% control of FHB in spikelets, regardless of product. Applications 5 to 7 days after anthesis provided less control than those at anthesis but achieved better control than preventative applications, which were applied before anthesis.
Table 1 Modified from Paul et al. 2018 to show the effects of fungicide application timing on Fusarium Head Blight Control and DON levels in winter wheat.
| Fungicide Application Timing | % FHB Control
(compared to non-treated) | % DON Reduction
(compared to non-treated) |
| Caramba at Pre-anthesis | 39 | 24 |
| Caramba at Anthesis | 52 | 39 |
| Caramba at 5-7 Days Post Anthesis | 48 | 41 |
| Prosaro at Pre-anthesis | 27 | 23 |
| Prosaro at Anthesis | 52 | 34 |
| Prosaro at 5-7 Days Post Anthesis | 38 | 31 |
Reductions in DON levels were most noticeable in applications at anthesis or post anthesis. (The study included wheat varieties with different levels of FHB susceptibility, including varieties classified as 'less susceptible'. Geographies included in the study spanned from Arkansas to North Dakota and eastward to Maryland.)
Specifically in Missouri, Dr. Kaitlyn Bissonnette's team, with support of the U.S. Wheat and Barley Scab Initiative, collected data in small plot research trials conducted at MU's Bradford Farm in 2019-2021 and Lee Greenley Jr. Memorial Farm in 2020-2021. Fungicide applications were made to wheat at 50% anthesis or 50% head emergence and plots were evaluated for FHB incidence and severity (Figure 2).
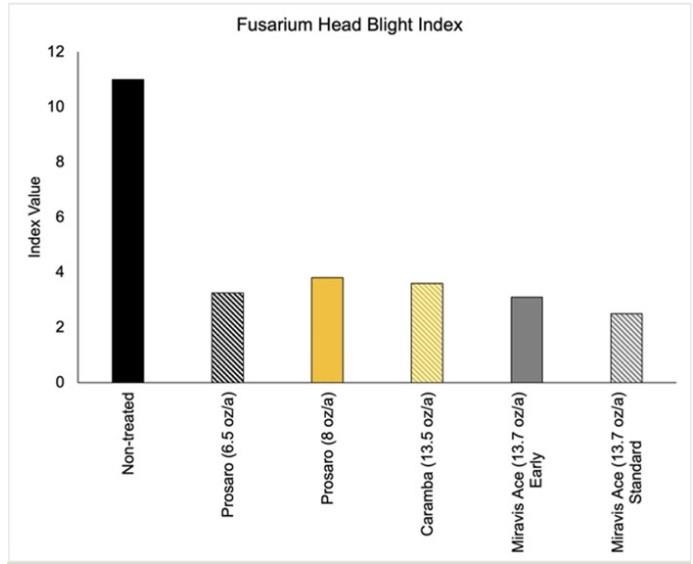
Figure 2 Fusarium Head Blight index consisted of incidences and severity measurements collected at 21 and 28 days after fungicide applications. Treatments were applied at anthesis except for the Miravis Ace early application, which was applied at 50% heading. Data is combined across 5 Missouri site years.
All fungicides reduced FHB. Miravis Ace has a longer application window that extends from 50% head emergence (Feekes 10.3) to 50% anthesis (Feekes 10.5.1) and was effective at regardless of the application timing. Prosaro had similar control levels for both application rates tested.
Wheat test weights were improved following all applications when compared to the non-treated (Figure 3). The highest test weights were associated with application of Miravis Ace at anthesis and the higher rate of Prosaro.
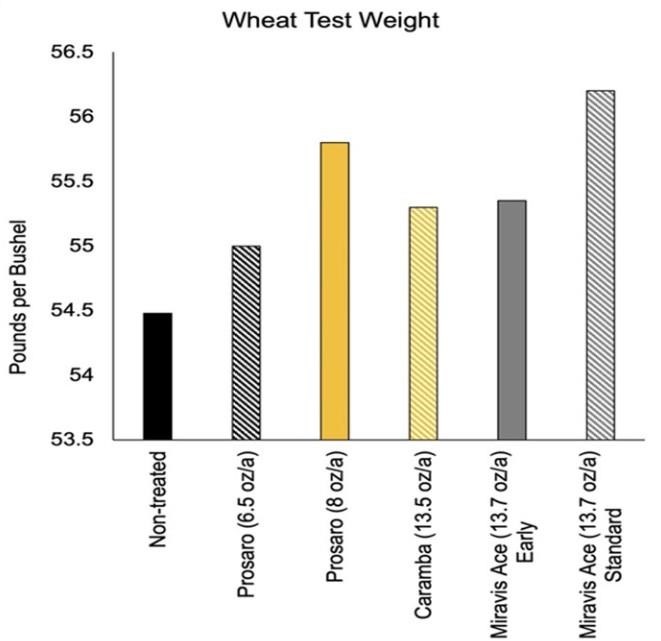
Figure 3 Wheat test weight following different fungicide treatments for Fusarium Head Blight. Treatments were applied at anthesis except for the Miravis Ace early application, which was applied at 50% heading. Data is combined across 5 Missouri site years.
Two new products are available for 2022. Spharex is a BASF offering that contains two active ingredients with demetyhylation inhibitor (DMI) activity. Prosaro Pro is a new Bayer CropScience offering with two types of active ingredients: 2 with DMI activity combined with a succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor (SDHI). Academic research on these products so far suggests similar efficacy to traditional products.
The environment is always going to play a factor in the extent of FHB severity and subsequent control. Environmental conditions that favor infection include frequent rain, high humidity, and temperatures in the range of 70's to mid-80's. Although April was cooler than normal and May has started out similarly, temperatures are forecasted to rise into the 80's next week. This may set us up for some 'interesting' situations with FHB. Extension tools available on this topic include:
Source : missouri.edu