Early prospects point to increased area for 2021 wheat crops but conditions are mixed.
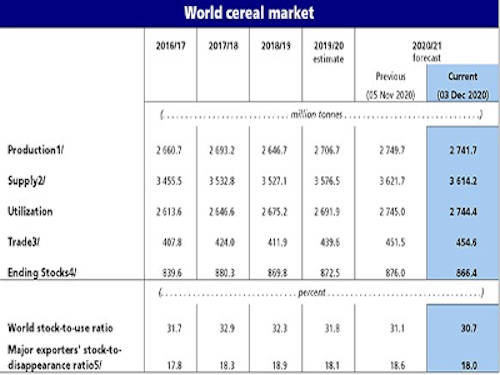
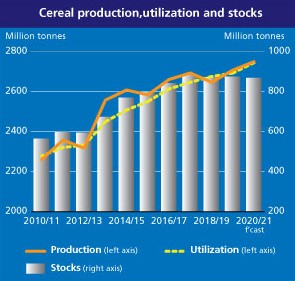
FAO’s forecast for global cereal production in 2020 has been lowered for the third consecutive month, with downward revisions for all the major cereals. Nonetheless, global cereal production is still expected to reach a record high level of 2 742 million tonnes, 1.3 percent above the previous year’s outturn.
Forecast at 1 472 million tonnes in 2020, world coarse grains production has been cut by 6.8 million tonnes month on month. The bulk of the revision reflects reduced yield prospects for maize in the United States of America (USA), which, however, is still on course to harvest its third largest crop on record, and in Ukraine. These reductions more than outweigh a lifting of Serbia’s maize production forecast, which is now seen to reach an all-time high in 2020. The forecast for world wheat production in 2020 has been trimmed marginally since last month to 761.7 million tonnes, putting this year’s output at a comparable level with the 2019 outturn. The downward revision reflects reduced forecasts for Argentina and Brazil, on account of recent sparse rains that curbed yield expectations, as well as in Kazakhstan, offsetting an increase made to the production estimate in the Russian Federation. As for rice, production prospects have deteriorated in Bangladesh and Viet Nam, in both cases reflecting the adverse impact of weather on secondary crops. However, the foreseen lower output in both countries, alongside other smaller downward revisions, are partly compensated by an upgrade for Pakistan, where preliminary official assessments indicate that another robust area expansion should lead to a record 2020 harvest. As a result, world rice production in 2020 is now predicted to reach an all-time high of 508.4 million tonnes, 1.5 percent above the 2019 reduced level but marginally down from the previous month’s expectations.
Looking further ahead, planting of the 2021 winter wheat crop in the northern hemisphere is underway, and sowings in several major producing countries are foreseen to increase driven by remunerative prices, although recent dry weather could curb planting expansions and hinder yields. In the USA, sowing operations are progressing at a fast pace, but dry weather conditions, influenced by the prevailing La Niña weather phenomenon, have resulted in moderately poorer crop conditions compared to the previous year. In Europe, robust export demand and rising prices have incentivized an area expansion in the Russian Federation, with sowings officially estimated at 19.2 million hectares, while limited rainfall in Ukraine caused 2021 sowings to fall to a below-average level. Following a reduced acreage in 2019, wheat sowings in the European Union (EU) are expected to recover substantially. In Asia, weather conditions have been generally conducive for the 2021 wheat crop and, supported by profitable prices, acreages in China, India and Pakistan are all foreseen to increase.
World cereal utilization in 2020/21 is forecast at a record 2 744 million tonnes, nearly unchanged from the previous month and 1.9 percent higher than in 2019/20. The forecast for total utilization of coarse grains in 2020/21 is pegged at 1 477 million tonnes, up 2.6 percent from the previous season stemming mostly from increased feed use, especially of maize and sorghum in China, as well as other uses, resulting from a rise in the production of maize-based ethanol in Brazil and the USA. At 757.6 million tonnes, global wheat utilization in 2020/21 is expected to exceed the estimated level for 2019/20 by 1.1 percent, largely as a result of a foreseen increase in food use. Global rice utilization in 2020/21 is anticipated to reach 510.3 million tonnes, unchanged from last month’s forecast and up 1.5 percent from 2019/20.
The forecast for world cereal stocks by the close of seasons in 2021 has been cut by 9.6 million tonnes since the previous month to 866.4 million tonnes, with stocks now seen falling below their opening level by 0.7 percent. At this level, the global cereal stock-to-use ratio would decline from 31.8 percent in 2019/20 to 30.7 percent in 2020/21, a five-year low but still a relatively comfortable level. At 402.5 million tonnes, total coarse grain inventories are seen lower by more than 10 million tonnes than earlier anticipated, largely reflecting a downward revision to maize inventories in the USA. With this month’s revision, world coarse grain inventories would fall by 2.8 percent below their opening levels. By contrast, the forecast for world wheat inventories has been scaled up by almost 2 million tonnes since November, mainly on expectations of larger stocks in Canada, China and the EU, and is now pegged at 282.9 million tonnes, up 2.3 percent from opening levels. Wheat stock buildups in China account for the bulk of the expected year-on-year expansion in global inventories. World rice stocks at the close of 2020/21 are pegged at 181.0 million tonnes, down 0.4 percent from their opening levels and 1.0 million tonnes below last month’s expectations. The monthly revision primarily reflects an anticipated decline in reserves in India owing to improved export prospects for the county. Stocks in India are nevertheless still predicted at an all-time record. Indeed, the expected accumulation in India, alongside an even higher than previously anticipated build-up in Thailand, is seen driving an increase in the major exporters’ aggregate rice reserves.
World trade in cereals in 2020/21 is forecast at 454.6 million tonnes, up 3.2 million tonnes from last month and now 3.4 percent higher than the 2019/20 level. The forecast for world trade in coarse grains in 2020/21 (July/June) is up 2.7 million tonnes month-on-month and is now pegged at nearly 223 million tonnes and surpassing the previous season’s record by 5.7 percent. This month’s upward revision primarily stems from a faster than expected pace in maize sales by the USA, driven by continued strong purchases by China. At 184.5 million tonnes, world wheat trade in 2020/21 (July/June) is forecast to remain near the 2019/20 level, unchanged since last month as greater expected sales from the Russian Federation balance a downward revision to Argentina’s exports as a result of lower crop prospects. World trade in rice in 2021 (January-December) is now forecast at 47.6 million tonnes, 6.9 percent above the revised 2020 forecast of 44.5 million tonnes. Upward import revisions are introduced for various Near Eastern and African countries this month, more than compensating for a somewhat less buoyant import outlook for the Philippines.
Summary Tables