To address these issues, a team of researchers developed a novel sensor that attaches directly to the underside of plant leaves. This small device uses a spectroscopic sensor and light source to measure leaf color without blocking sunlight, and it can track changes in the same spot over time. Powered by a battery, with Wi-Fi data transfer and waterproofing, the sensor can work outdoors for over a month, allowing for extended data collection.
The research is published in Sensing and Bio-Sensing Research.
"Smart agriculture is a huge time-saver," says Ko-ichiro Miyamoto, "Farmers don't have time to manually check every single plant. This sensor is able to provide fine-tuned readings for what's going on in real time. Then, they can react accordingly to areas where plants are experiencing high levels of stress."
This sensor performed well when compared with a commercial spectrometer on about 90 leaves from 30 different plant species. It accurately distinguished colors across seven out of its eight detectable wavelengths, and its readings at 620 nm were highly similar to commercial chlorophyll meters.
Further tests with a stress-sensitive Arabidopsis thaliana mutant showed that changes at 550 nm in the sensor's readings matched the plant's stress responses, which aligned with the commonly used Photochemical Reflectance Index (PRI).
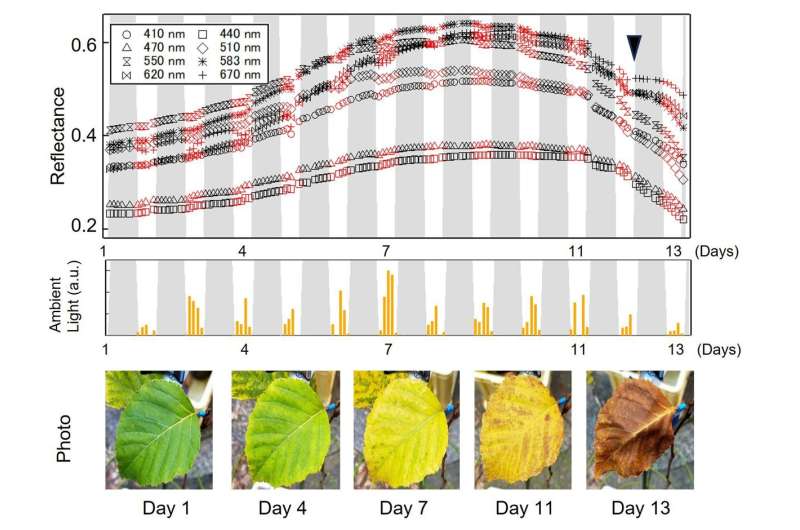
In an outdoor trial to test performance under real life conditions, they attached the sensor to birch leaves to track changes in leaf color during autumn, leaf fall, and aging over two weeks. They were able to observe a decrease in chlorophyll (an indicator of plant stress) and how the plant's response fluctuated with sunlight intensity.
Click here to see more...