By Dean Malvick
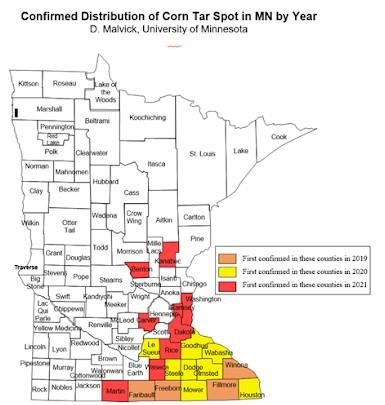
Tar spot of corn increased in distribution and severity in Minnesota in 2021 compared to previous years. It developed widely in SE MN where it developed previously, and spread west and north to areas where it was not previously known. Thus, tar spot is no longer restricted to southeast Minnesota and may pose a risk to more areas in the future.
Tar spot is a fungal disease of corn that primarily infects and damages leaves. It can result in significant yield losses, depending on weather, severity, and timing of disease development. Risk of disease is highest in areas with frequent rains where the disease has occurred previously. Corn tar spot is caused by the fungus Phyllachora maydis. It produces raised, small (0.1” – 0.2”) raised, irregular-shaped black structures on leaves. The black structures are firm, appear mostly smooth on the surface, and do not rub off or break open (see photos below from MN corn fields).