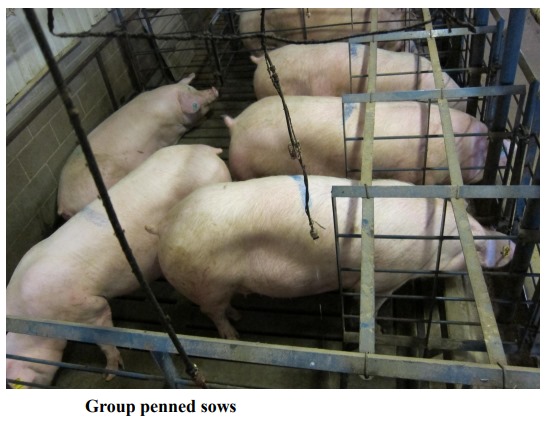
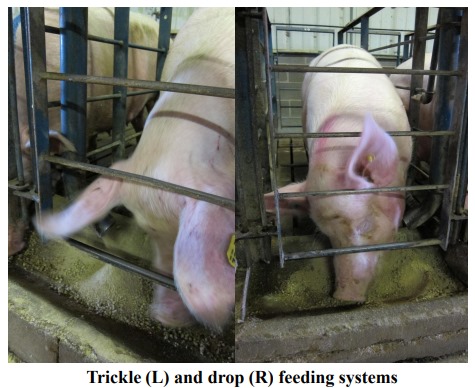
Crates are banned for pregnant gilts and sows in Europe and several USA states based on the public’s view of pig welfare. Group pens are believed to enhance welfare because pigs have more space and freedom to move. In addition, they are able to express social behaviors with their pen mates. However, competition and fighting among pigs may be observed if their limited ration of feed is not delivered in a protected manner. Food competition may result in injuries, stress, and poor reproductive performance. The trickle feeder delivers feed at a rate that allows the slowest eating gilt/sow to consume all of her limited ration without competition from other gilts/sows. Since there are few published studies in the USA concerning the efficiency trickle feeding, and especially because no work has been published using the now-common genotype -- Landrace x Yorkshire or Camborough genetic line —the objective was to investigate the efficacy of individual crates or group penning compared to a single drop feeder/pen or crate for pregnant gilts. Measures included in this project were behavior, blood parameters, reproductive performance, and skin injuries. The findings will be directly relevant to this society issue.
Abstract
A randomized complete block design experiment with 2 × 2 factorial rearrangement of treatments was conducted to study the effect of 2 housing systems, group pens and crates and 2 feeding systems, single drop and trickle feeding systems on lactating sow reproductive performance, litter performance, behavior, physiology and skin lesion scores. A total of 40, Camborough (Yorkshire x Landrace) gilts were allocated into groups of 5/pen or crates. Behaviors such as feeding, drinking, standing/walking, lying, sitting, agonistic behavior, and oral-nasal-facial (ONF) behavior were video recorded for 24 h at 50 to 60 d of gestation and transformed before analyses. Behavior data were collected hourly based on a 5 min interval between scan samples. Whole blood was collected via jugular puncture over heparin for determinations of plasma cortisol, white blood cell counts, % differential WBC count, neutrophils:mononuclear cell ratio, neutrophil phagocytosis, and neutrophil oxidative burst a week after behavioral observations. No significant differences were identified among housing and feeding systems for reproductive or physiological measures (except for plasma cortisol, neutrophil phagocytosis, and neutrophil oxidative burst that had not yet been assayed). Gilt ONF behavior was higher (P < 0.05) among crated gilts than penned gilts (LSmeans 12.7 ± 1.13 vs. 7.6 ± 1.19%). The interaction between penning and feeding system was significant for head lesion score (LSmeans for pen-drop, pen-trickle, crate-drop, crate-trickle were, respectively: 1.0 ± 0.07, 0.0 ± 0.06, 0.0 ± 0.06, and 0.13 ± 0.06; P < 0.01). Crated and grouppenned sows had similar reproduction. With only minor differences in skin lesion score, each sow penning/feeding system supported similar sow welfare. However, the finding that Camborough gilts had more ONF behavior in crates (than pens) and more head skin lesion score in pens (than crates) differed from our previous work with Camborough-22 gilts in which these differences were not observed. Genotypes may respond differently to group housing than individual housing.


Method
After artificial insemination, gilts were allocated to the treatment groups. Four treatment groups were examined: 1) Crate + trickle feeding, 2) Crate + drop feeding, 3) Pen of 5 + trickle feeding, and 4) Pen of 5 + drop feeding This experimental model was used before to evaluate the welfare of different housing systems (Hullbert and McGlone, 2006). This study was unique in that it utilized a new genetic line that was becoming the most common genetic line in the USA swine industry. This was the Camborough which is a Yorkshire X Landrace cross that was unique to PIC (a pig breeding stock company).
Measures were collected of reproductive performance, behavior, skin lesion score, and physiology over two pregnancies.
Behavioral observations of gilts were performed from video recordings during mid gestation (a 24-hour sample of behavior with a focus on stereotyped oral-nasal-facial behaviors along with feeding, drinking, standing/walking, sitting, lying down, and agonistic behavior). Blood was collected from the jugular vein one week after behavior data collection to determine cortisol concentrations, total and differential white blood cell counts, neutrophil oxidative burst and phagocytosis (measures of stress).
Reproductive measures such as farrowing rate, litter size, number of piglets born alive, number of stillborn piglets, number of mummified piglets, piglet birth weight, number of weaned piglets, piglet weaning weight, sow weaning weight, backfat at breeding, farrowing, and weaning were recorded. In addition, skin lesion scores were determined 3 days after weaning. From farrowing to weaning, all gilts were housed in standard farrowing crates.
.png)
After weaning sows were returned to the same gestation system for their second pregnancy. The data report here are for parity 1 only.
Housing systems (group pens vs. individual crates) and feeding systems (drop or trickle) did not significantly affect the majority of measures for reproduction, production, and welfare of sows. However, group pen sows developed significantly higher head lesion scores than crated sows. ONF behavior was significantly higher in crated sows than group penned sows. Overall, individually-crated and group penned sows had similar welfare.
To read and download full report in PDF
Please click here